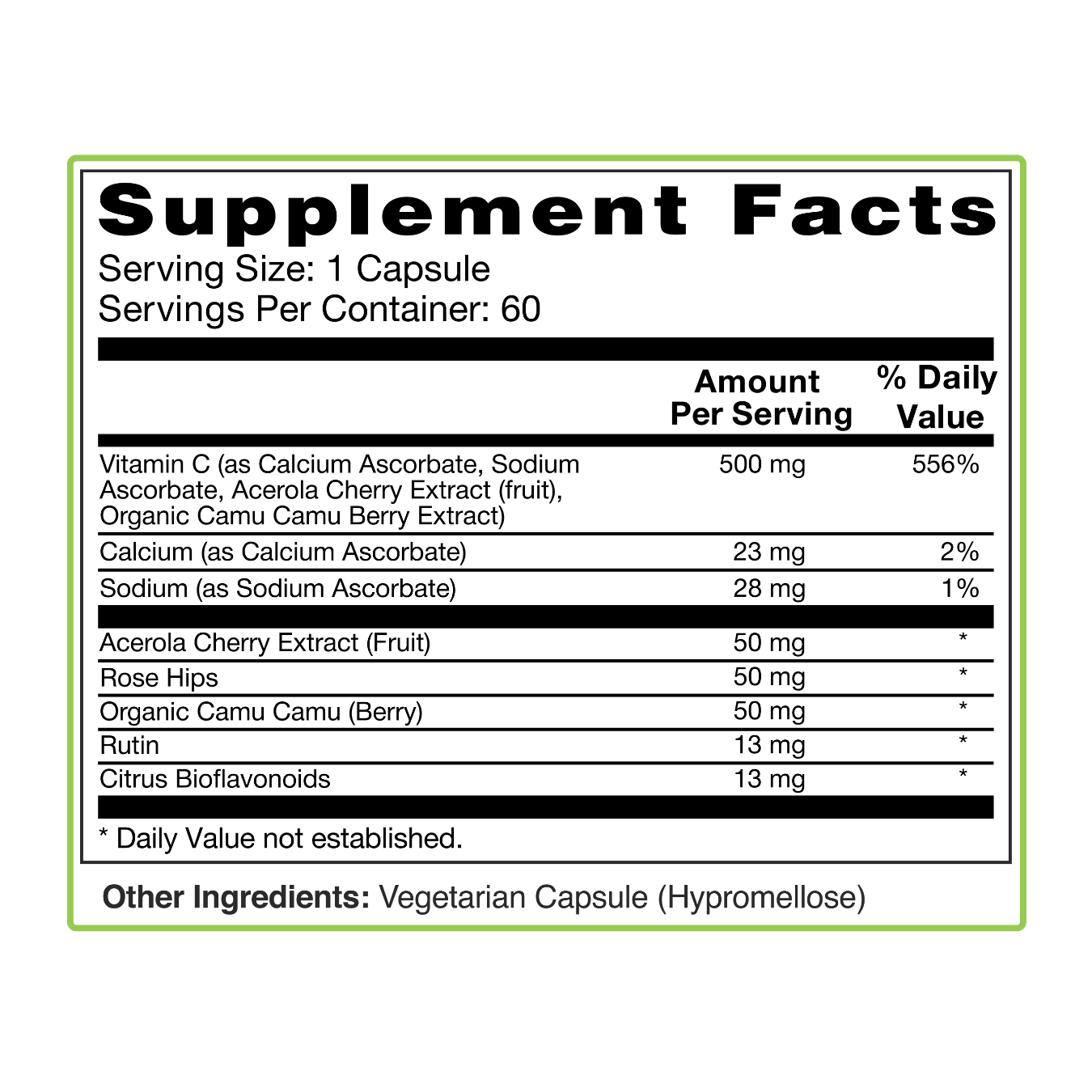
Active-C is a high-quality vitamin C supplement formulated with a synergistic blend of buffered vitamin C (Calcium Ascorbate and Sodium Ascorbate), whole-food concentrates (Acerola, Rose Hip, and Camu Camu), and natural antioxidants like rutin and citrus bioflavonoids.
This carefully crafted combination helps support absorption, reduce gastrointestinal discomfort, and deliver a full spectrum of health benefits.
Unlike traditional ascorbic acid supplements, Active-C offers a gentler, more bioavailable approach by pairing water-soluble vitamin C with nutrient-dense plant sources.
This comprehensive blend supports:
Immune resilience, healthy collagen levels, cardiovascular health, and antioxidant defense at a cellular level
Developed by healthcare professionals, Active-C delivers research-backed efficacy with a focus for you.